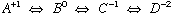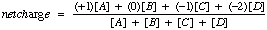Biol/Chem 5310
Lecture: 5
September 5, 2002
Amino Acids
Proteins were the first studied macromolecules.
The roles of proteins include:
enzymes
binding/transport
structural
mechanical
gene expression/protein synthesis
hormones
antibodies
Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides.
Polypeptides are linear polymers of amino acids.
20 standard amino acids in proteins
General structure of an amino acid, zwitterionic form
Peptide bond: amide linkage of amino acids, head to tail, called a peptide bond
Note reduction in charge when peptide bond forms.
Amino acids are always charged at pH 7
Polypeptides are reduced to one amino group and one carboxyl group per chain, plus the side chains of each amino acid residue.
Classification of amino acids
Structures
Nonpolar side chains
Glycine, Gly, G
smallest, no side chain, only nonchiral aa, flexible in protein chain
Alanine, Ala, A
side chain aliphatic (methyl), small, common aa
Valine, Val, V
side chain aliphatic (isopropyl), somewhat hydrophobic, branched at b-carbon
Leucine, Leu, L
side chain aliphatic, hydrophobic, common, branched at g-carbon
Isoleucine, Ile, I
isomer of Leu, side chain aliphatic, hydrophobic, branched at b-carbon
Methionine, Met, M
side chain thioether, hydrophobic, flexible like straight chain aliphatic, first amino acid in synthesized protein chain
Proline, Pro, P
an imino acid, side chain is a ring that forms a secondary amine, properties in proteins dominated by the restrictions imposed by the ring
Phenylalanine, Phe, F
side chain aromatic (phenyl), hydrophobic, absorbs uv
Typtophan, Trp, W
side chain aromatic (indole), hydrophobic, 1 H-bond donor (N-H), absorbs uv
Polar uncharged side chains
Tyrosine, Tyr, Y
side chain aromatic (phenolic), hydrophobic and polar, OH is H-bond donor and acceptor, absorbs uv, side chain can ionize, pKa = 10.5
Cysteine, Cys, C
side chain somewhat hydrophobic (sulfhydryl), weak H-bonds, usually as acceptor, -SH can ionize, pKa = 8.4, found in enzymes at active sites, 2 SH groups can form a disulfide bond
Serine, Ser, S
side chain alcohol, small, very polar, H-bond donor and acceptor, structural analog of Cys, but does not ionize, sometimes found in enzymes at active site
Threonine, Thr, T
side chain alcohol, somewhat polar, branched at b-carbon, isosteric with valine, like Ser H-bond donor and acceptor but not as likely to be at active site
Asparagine, Asn, N
side chain amide, very polar, extensive H-bonding, does not ionize, but can deamidate in acid (Asx)
Glutamine, Gln, Q
similar to Asn, side chain amide, very polar, extensive H-bonding, does not ionize, but can deamidate in acid (Glx)
Charged polar side chains
Aspartic acid, Asp, D (aspartate)
side chain carboxyl, small, negative when ionized (pH 7), pKa = 3.9, isosteric with Asn
Glutamic acid, Glu, E (glutamate)
side chain carboxyl, similar to Asp, pKa = 4.1, isosteric with Gln
Lysine, Lys, K
side chain, long flexible aliphatic, e-amino group, positive charge at pH 7, pKa = 10.5
Arginine, Arg, R
side chain contains guanidinium group, positive charge at pH 7, pKa = 12.5, multiple H-bond donors
Histidine, His, H
side chain imidazole, weak base, pKa = 6.0, partially ionized at pH 7, positive charge when ionized, commonly found in enzymes
QUIZ of properties
Quiz of structure
Ionization of amino acids
Side chain does not ionize
charge +1, pKa = 2-3, charge 0, pKa = 9-10, charge -1
pI= pH at which net charge is zero, called isoelectric point
here it is the average of pKa1 and pKa2
Side chain ionizes, e.g. Asp
charge +1, pKa1=2.0, charge 0, pKa2=3.9, charge -1, pKa3=9.9, charge -2
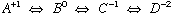 The positive species (A) must exactly cancel the two negative species (C and D).
If A is present, the pH must be low, near the pKa1.
In this case, D will be extremely low. About 10 to the 8th less than C
What is pI?Average of pKa1 and pKa2.
When the pH equals the pI, the net charge of the molecule is zero.
In general,
The positive species (A) must exactly cancel the two negative species (C and D).
If A is present, the pH must be low, near the pKa1.
In this case, D will be extremely low. About 10 to the 8th less than C
What is pI?Average of pKa1 and pKa2.
When the pH equals the pI, the net charge of the molecule is zero.
In general,
Stereochemistry of amino acids
The a-carbon is a chiral center (except Gly)
Gly has 2-hydrogens bonded to its a-carbon, it is superimposable on its mirror image.
All other amino acids have 4 different substituents
The 20 standard amino acids are L-form, enantiomers are called D-form (Fischer convention)
Ile and Thr have a 2nd chiral center
RS system (Cahn-Ingold-Prelog)
Rank the 4 substituents of a chiral center
-SH> -OH> -NH2> -COOH> -CHO> -CH2OH> -C6H5> -CH3> H
Orient the lowest priority group away
If decreasing priority is clockwise: R
If decreasing priority is counterclockwise: S
All L-amino acids are S, except Cys
Try a quiz
in Chapter 4.
Comments/questions: svik@mail.smu.edu
Copyright 2002, Steven B. Vik, Southern Methodist University