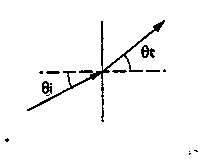
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
SOUTHERN METHODIST UNIVERSITY
FIBER OPTIC TELECOMMUNICATIONS
SMU EE 5303 NTU TM-513-N FINAL May 6, 1997
Name (print): ________________________
Location: ________________________
Date and Time Exam taken: ________________________
Note #1: please indicate your location: (NTU, TAGER, Video Distance, Video on Campus, or Campus-live) and the date and time of the exam above
Note #2: some of the multiple choice questions may have more than one correct answer listed. If so, circle all of the correct responses for the question.
Note #3: please print your name at the bottom of the remaining pages.
Note #4: please provide a brief explanation of your answers to multiple-choice type questions.
Note #5: several figures are shown on the last pages that could be helpful in solving some of the problems below.
Note #6: each question is worth 3 points unless otherwise stated.
Note #7: proper units must accompany numerical answers for full credit
TIME: The allowed time period is 180 minutes (3 hours).
CONSTRAINTS: This exam is closed to books and notes with the exception below:
ALLOWED: 3 page of notes (81/2 x 11; can write on both sides); calculator; straight edge; ruler; and compass.
NOTE TO SITE COORDINATORS AND/OR PROCTORS:
THIS EXAM CONTAINS 19 PAGES AND 34 PROBLEMS--make sure all the pages are included.
IF THIS EXAM WAS FAXED TO YOU, make sure that each page is readable
. There should be a minimum margin of one-half inch on all four sides. If this is not the case, please call Shirley Braun and request that the exam be sent again.YOUR SIGNATURE IS REQUIRED ON PAGE 15.
Please check that the student’s name appears on the bottom of each page (particularly important if you return the exam by fax.)
1. The AlGaAs semiconductor lasers used in CD players have a wavelength of 0.78 µm. i) how many photons/sec are produced by the laser if the output power is 3 mW? ii) the new DVD (digital video disc) technology uses InGaAlP semiconductor lasers with a wavelength of 630 nm. At 3 mW output power, will these DVD lasers generate more or less photons than CD lasers?
2. When an electromagnetic wave propagates from one medium with an index of refraction of n1 = 2.5 into a second medium with an index of refraction of n2 = 1.8,
a) only the frequency changes,
b) only the wavelength changes,
c) both the frequency and the wavelength change, and/or
d) the frequency and the wavelength both remain the same.
Briefly explain your answer:
3. A WDM (wavelength division multiplex) system is proposed that will have 17 channels (wavelengths) equally spaced 100 GHz apart. The center wavelength is 1.53 µm. What is the wavelength spacing () between the center wavelength and the next wavelengths on either side of the central wavelength?
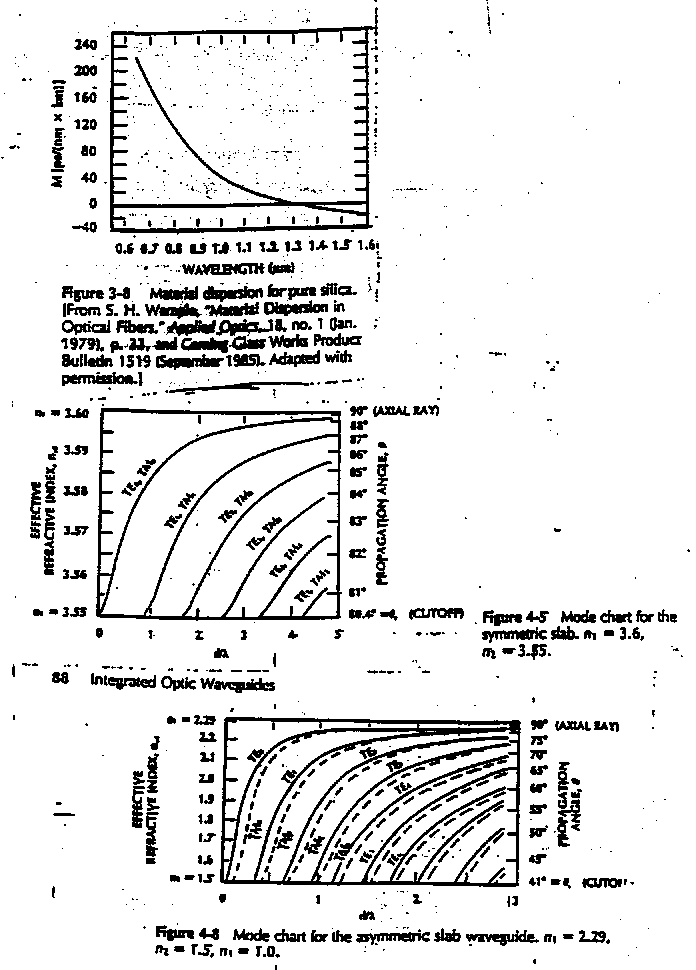
4. Briefly explain material dispersion.
5. Briefly explain waveguide dispersion.
6. Briefly explain modal distortion.
7. A lens system is used to collect the light from a laser diode source (which has an angular spread of 42°) into an optical fiber with an acceptance angle of 8°.
i) what is the resulting magnification of the lens system?
ii) if the diameter of the optical spot at the laser facet is 3 µm, and the core of the fiber is 10 µm, will the image of the optical spot at the facet be larger than, equal to, or less than the core of the fiber?
8. i) a light ray with a wavelength of 0.78 µm proceeds from air into AlGaInAs (n2 = 3.6). If the incident angle is i = 7°, what is the transmission angle t ?
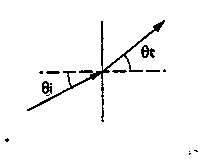
ii) now consider a light ray going from AlGaInAs into air with the same incident angle. What is the resulting transmission angle
t ?
9. i) what is the critical angle for a ray in AlGaAs (with an index of 3.45) if the material outside the AlGaAs is air?
ii) What is the criteria for a critical angle to exist between two media with indices of refraction n1 and n2?
10. A semiconductor laser emits optical radiation with a free space wavelength of 1.57 µm. What is the i) frequency, ii) velocity, and iii) wavelength of the optical radiation inside the semiconductor laser? Assume that the index of refraction of the semiconductor laser material is 3.47.
11. What is the maximum number of analog phone calls (voice channels) that can possibly be squeezed onto an optical fiber if the light has a wavelength of 1.55 µm? (be sure to state any assumptions.)
12. A 5 W argon laser with a wavelength of 0.3411 µm has a spot size (2w
o) of 3 mm and is aimed at one of the reflective stop signs at the intersection of Caruth and Airline from a distance of 1000 meters. Assume that the light distribution from the argon laser is Gaussian. What is the spot size (2w) of the beam at the stop sign? (Is the beam smaller or larger than the stop sign?)
13. A lens with a focal length of 0.5 cm is used to focus light with a wavelength of 630 nm to a spot. In one case, light of a uniform intensity (across the lens) is focused. In the second case, light with a Gaussian distribution (across the lens) is focused.
i) describe the distribution of the light at the focus in both cases.
ii) which intensity distribution at the lens results in the smallest spot size at the focus?
14. The index of refraction in an optically transparent material is given by:
n(
) = 2.0 - 0.1 for 0.7 µm < 3.0 µm
a) what is the index of refraction of this material at a wavelength of 1.3 µm?
b) what is the phase velocity of an optical wave propagating in this material if the wavelength of the light is 1.3 µm?
15. For the same optically transparent material described in problem 14, find a mathematical expression for the group index for optical waves with wavelengths between 0.7 µm and 3.0 µm.
16. For the same optically transparent material described in problem 14, calculate the pulse spreading if an optical pulse with a wavelength of 2.3 µm and a bandwidth
= 15 nm travels a distance of 25 km.
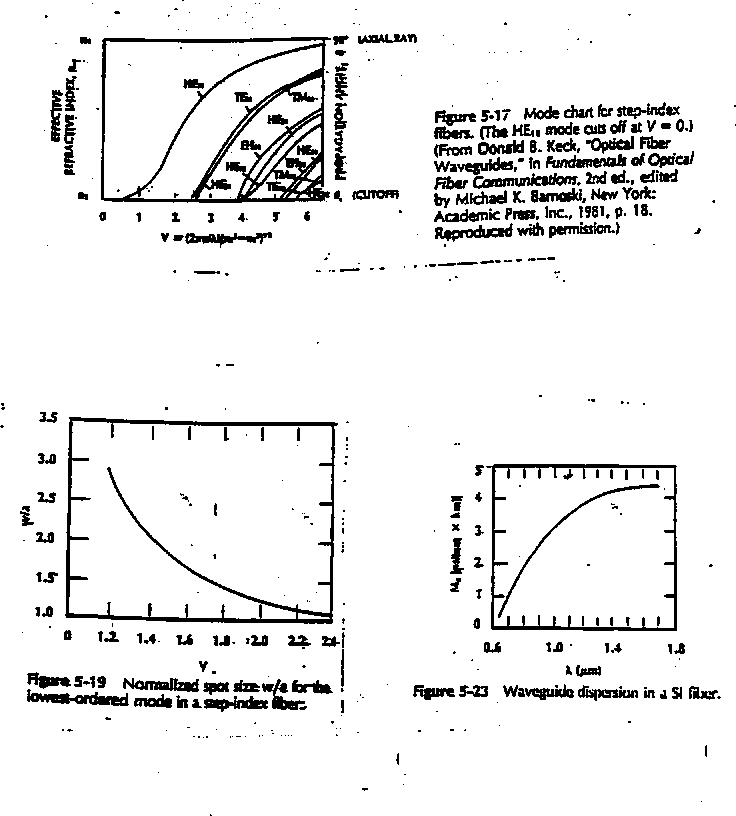
17. Consider a symmetric slab waveguide (or a circular step-index fiber waveguide). If all parameters are held constant except the index of the core decreases, will the number of propagating modes increase or decrease? Briefly explain.
18. Consider a symmetric slab waveguide (or a circular step-index fiber waveguide). If all parameters are held constant except the wavelength increases, will the fraction of the energy (of the fundamental propagating mode) in the cladding regions increase, decrease, or remain the same? Briefly explain.
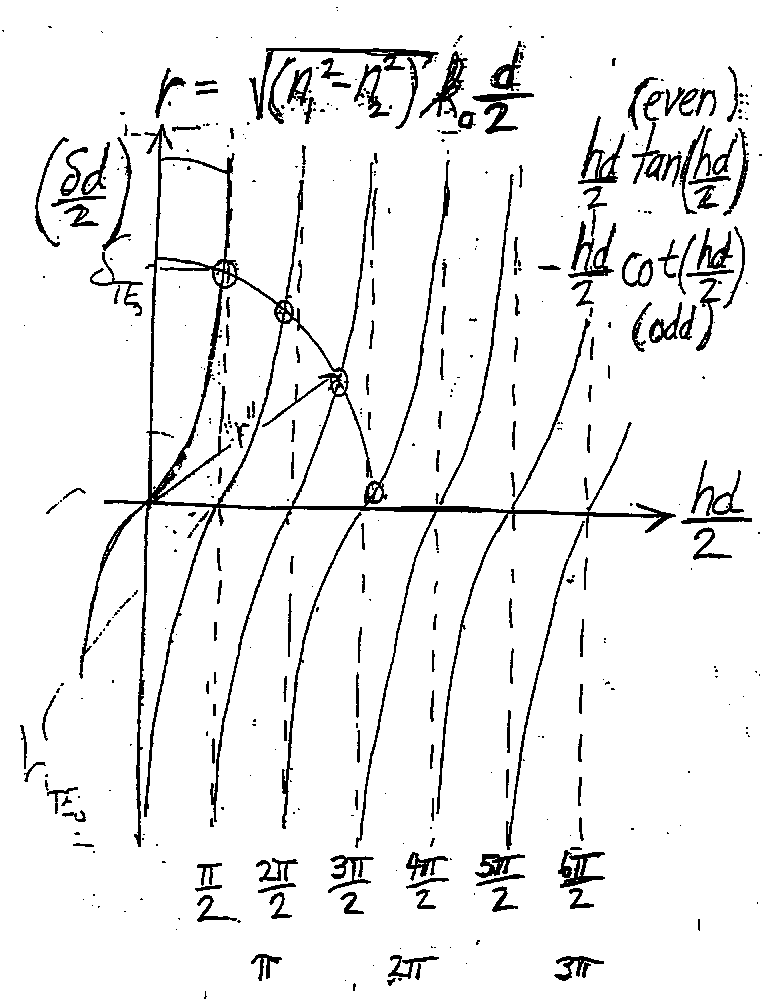
19. The middle layer of a three-layer symmetric slab waveguide has a thickness of 3 µm. The wavelength of light propagating in the waveguide is such that 7 modes can propagate. For this waveguide, a) qualitativley sketch the TE2 field distribution, and b) qualitativley sketch the TE4 intensity distribution. c) which mode (TE2 or TE4) has the higher effective index?
20. The answer is 2.405. What is the question?
21. Qualitatively sketch a) the index of refraction, b) the first derivative of the index of refraction, and c) the second derivative of the index of refraction as a function of wavelength (over the range 0 to 3 µm) for a typical glass (such as quenched SiO2) that is used in making optical fibers.
22. On the same graph, qualitatively sketch and label both the index of refraction and the group index of refraction for the same glass discussed in problem 21.
23. Find the contribution to pulse spreading in a standard step index fiber (n1 = 1. 67 and n2 = 1.57, V = 2.25) which is due to material dispersion if the optical source is a laser operating at a free space wavelength of 1.57 µm. The dfb laser has a spectral emission width of 0.1 Å. The length of the silica fiber is 25 km. The fiber is made from quenched SiO2.
24. Consider the same standard step index fiber (n1 = 1. 67 and n2 = 1.57, V = 2.25) described in problem 23.
a) find the amount of pulse spreading in the fiber due only to waveguide dispersion if the optical source is a laser operating at a free space wavelength of 1.57 µm. The dfb laser has a spectral emission width of 0.1 Å. The length of the silica fiber is 25 km. The fiber is made from quenched SiO2.
b) what is the total (material and waveguide) dispersion for this fiber?
25. What is the 3-dB optical bandwidth of the system described in problems 23 and 24?
26. A step-index fiber with a core and cladding index of n1 = 1. 67 and n2 = 1.57 has a V number of 25. What is the pulse spread due only to energy being distributed among multiple modes for a 30 km fiber if the optical source is a laser operating at a free space wavelength of 1.57 µm with a spectral width of 0.1 Å? The fiber is made from quenched SiO2.
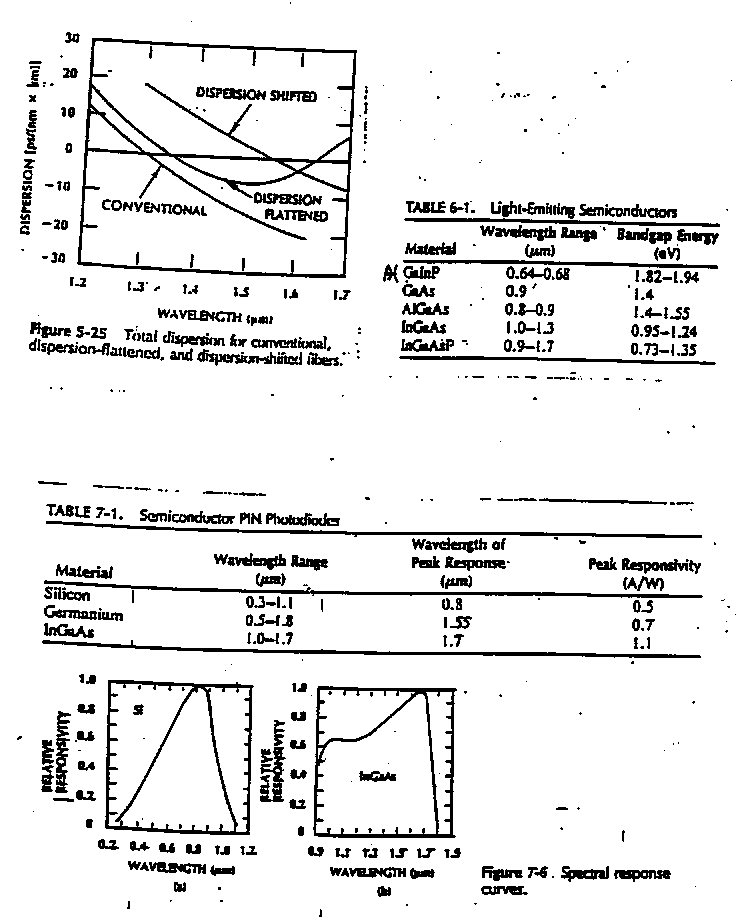
27. Briefly discuss dispersion-shifted and dispersion-flattened fibers. Indicate a possible index profile for each type.
28. Which of the following waveguides can be designed so that no optical mode can propagate? Another way to ask this question is which waveguides can be designed to have all modes below cut-off? (Assume a finite, non-zero slab or core thickness and that the core or inner region has a higher index than the cladding regions.)
a) symmetric slab waveguides
b) step-index circular fiber waveguides
c) asymmetric slab waveguides
29. An ideal laser diode has a threshold current of 12 mA and a "slope efficiency" of 0.25 mW/mA.
i) Sketch the light (optical output power) versus drive current for this device for a current range of 0 to 100 mA.
ii) How much optical power is emitted at a drive current of 50 mA?
30. You have to use an LED with a central wavelength of 0.85 µm as a source for a fiber system. You can choose between single-mode SI, single-mode GRIN, multi-mode SI, and multi-mode GRIN fibers. The core diameters and the
ns are the same for the single-mode fibers, and the core diameters and the ns of the multi-mode fibers are the same. You are more concerned with data rate than with the difficulty of coupling the LED to the fiber. Which fiber would you choose and why?
31. You are using 17 DFB lasers as sources for a WDM fiber system. You can choose between single-mode SI, single-mode dispersion flattened, multi-mode SI, and multi-mode GRIN fibers. The core diameters and the
ns are the same for the single-mode fibers, and the core diameters and the ns of the multi-mode fibers are the same. Which fiber would you choose and why?
32. For a fiber system that uses Honeywell VCSELs (with a lasing wavelength of 0.85 µm) as optical sources, would you choose a Si, InGaAs, or Ge detector? Explain your choice.
33. An InGaAs PIN photodiode has a responsivity of 0.6 A/W at a wavelength of 1.55 µm. If 80 µW of 1.55 µm radiation are incident on the detector, what current (ideally) flows through the load resistor in a simple PIN circuit?
This final problem is worth only 1 point:
34. The principle of least time can be used to derive
a) Snell's law,
b) the law of refraction,
c) the law of reflection,
d) the thin lens equation,
e) the graded index profile of a GRIN lens
f) the index profile of a GRIN lens
g) the best path for a lifeguard to rescue a drowning person
CERTIFICATION OF TESTING ENVIRONMENT:
I certify that I have completed this test in the 90 minute time period allotted, and that I have neither given nor received help from another person, nor have I had advanced access to questions or answers.
Signed:________________________date:________
SITE COORDINATORS AND/OR PROCTORS:
I distributed and collected this test in a 180 minute (3 hour) interval
on_______________________________(date).
Signed__________________________________
Site Coordinator/Proctor must sign