The Asp shown in purple is the site of N-linked glycosylation. The yellow residues form an intramolecular disulfide bond. These interactions occur in each monomer and contribute to protein stability. Disulfide Bond Between Monomers
At Cys603, the two monomers associate with each other via a disulfide bond. This occurs in the extracellular domain. Leucine Plug
Leucine 554 acts like a plug when BCRP is in its inward-facing state. This plug serves to create two cavities, one larger than the other. The larger cavity was found to be the drug/substrate binding pocket. The size and shape of this cavity favors binding of flat and hydrophobic molecules.
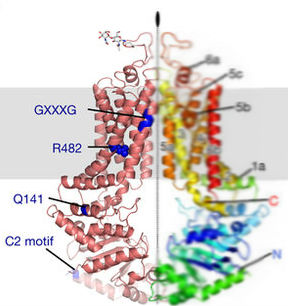

These images depict the motifs present in BCRP. The NPxDF (here 298-NPADF-293) motif is conserved across all of the G subfamily. The Signature motif is present in ABC transporters. The other motifs play roles in binding and catalysis, but further study is needed. (See the next page for source reference of the right image.)