|
OPTNET is a program for identifying the minimum-cost solution of network flow problems. The user enters a model title and list of arcs in the network. Pressing the Solve LP button runs OPTNET and displays the generated reports
Model input format. The title of the model is entered into the indicated form field. A network flow problem is given in circularized form (see below) and is entered in the Model Input Field as series of directed arcs, one per line.
Each model arc is given in one of the following forms:
- from-node to-node unit-cost upper-bound lower-bound
- from-node to-node unit-cost upper-bound
- from-node to-node unit-cost
- from-node to-node
where:
- from-node: name of the arc’s originating node, 1-8 letters and digits, beginning with letter
- to-node: name of the arc’s terminating node, 1-8 letters and digits, beginning with letter
- unit-cost: (integer) cost per unit of flow across or through the arc (assumed to be 0 in Form 4)
- upper-bound: (integer) maximum possible flow through the arc (assumed to be 9999999 in Forms 3 and 4)
- lower-bound: (integer) minimum required flow through the arc (assumed to be 0 in Forms 2, 3, and 4)
Model limits. The model cannot exceed 400 nodes and 2000 arcs. All numerical values must be specified as integers.
Example model. (This model can be cut and pasted into the input form)
SOURCE A 0 100 100
SOURCE B 0 200 200
A D 30
A C 10
B C 5
B E 25
C D 18
C E 20
D SINK 0 150 150
E SINK 0 150 150
SINK SOURCE
Circularized network models. OPTNET requires that networks be described in a circularized network form, which does not use supplies and demands on nodes. Instead it requires that all flow that enters a node must leave, hence the net supply and demand at a node is zero. This is a circularized network graph for the above example model.
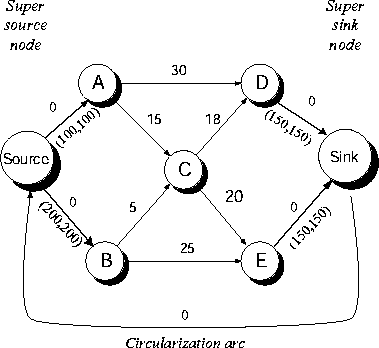
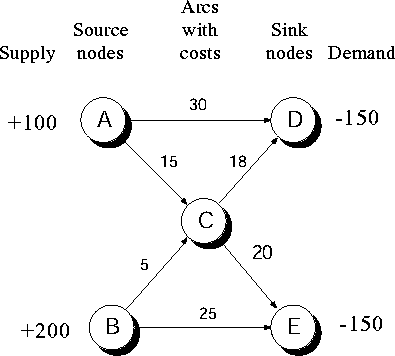
Any network with supplies and demands at the nodes can be converted into circularized form by adding two new nodes and a few arcs. The figure above shows a circularized form of the following network graph with supplies and demands at the nodes.
Example 2: Stuart Furniture network
Formulation of the Stuart Furniture case, with costs given in cents and the units of flow are chairs or chairs-worth of wood.
source s1 200 10000 400
source s2 150 10000 400
s1 p1 20
s1 p2 40
s1 p3 80
s1 p4 80
s2 p1 80
s2 p2 60
s2 p3 20
s2 p4 20
p1 p1a 500 500
p1 p1a 600 250
p2 p2a 700 750 400
p2 p2a 900 250
p3 p3a 300 1000 500
p3 p3a 400 400
p4 p4a 400 250 250
p4 p4a 500 100
p1a ny 100
p1a dal 100
p1a sf 200
p1a chi 0
p2a ny 300
p2a dal 600
p2a sf 700
p2a chi 300
p3a ny 300
p3a dal 100
p3a sf 500
p3a chi 300
p4a ny 800
p4a dal 200
p4a sf 100
p4a chi 400
ny sink -2000 2000 500
dal sink -1500 400 100
sf sink -2000 1500 500
chi sink -1800 1500 500
sink source
|