|
DTree analyzes decision trees and determines the optimal set of decisions based on expected values.A decision tree consists of a set of (a) decision nodes with decision branches or arcs, (b) chance event nodes with event branches, and (c) payoffs to be received from a series of decisions and events.
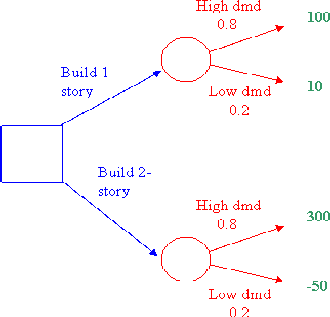
Example. An engineering manager must decide whether to build a one- or two-story facility. The payoff from each choice depends on whether demand is high or low, and the P(high) = .8 and P(low) = .2. The tree can be depicted as follows, with the decision nodes and arcs/branches in blue, the event nodes and arcs in red, and the payoffs in green.
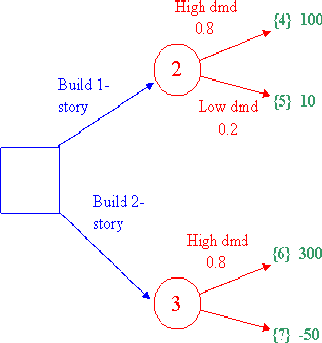
By adding nodes for each payoff and numbering the nodes, starting with 1, the decision tree input to DTree is as follows.
Model Input Requirements
DTree input consists of a list of arcs from this expanded tree, one arc or branch per line, plus one line for each payoff, as follows:
Decision branch or arc: D fromnode tonode arcid description
Event branch or arc: E fromnode tonode probability arcid description
Payoff: P node payoff
where
- fromnode: number of node where arc begins
- tonode: number of node where arc ends (arrowhead points to)
- arcid: 4-character identifier for this arc
- description: (optional) longer description of the branch or arc
- probability: likelihood of this event happening
- payoff: payoff received if this node is reached
Limits: program is limited to 99 nodes (decision nodes, chance event nodes, payoffs) and 98 arcs.
DTree Output
DTree analyzes the problem and gives the following:
- Branch report, listing each decision or event arc and its characteristics
- Decision tree diagram, showing decision nodes in square brackets, chance event nodes in parentheses, and payoff nodes in curly brackets. Non-optimal decision branches are indicated with an x.
- Node Summary Report, for the evaluated and optimized tree, each node and its payoff or expected payoff value if the optimal strategy is followed
- Optimal strategy: the decision(s) to follow to maximize expected payoff.
DTree input data for above example:
D 1 2 Bld1 Build one-story
D 1 3 Bld2 Build two-story
E 2 4 .5 HiDm High demand
E 2 5 .5 LoDm Low demand
E 3 6 .5 HiDm High demand
E 3 7 .5 LoDm Low demand
P 4 100
P 5 10
P 6 300
P 7 -50
Other example problem data:
|